AWS for Genomic Insights
Scaling Annotation Pipelines with AWS
Organization
The University of Chicago
Core Technologies
AWS Lambda AWS DynamoDB AWS EC2 AWS S3 SNS SQS AWS Step Functions
Domain
Cloud Computing
Date
May 2024
Technical highlight
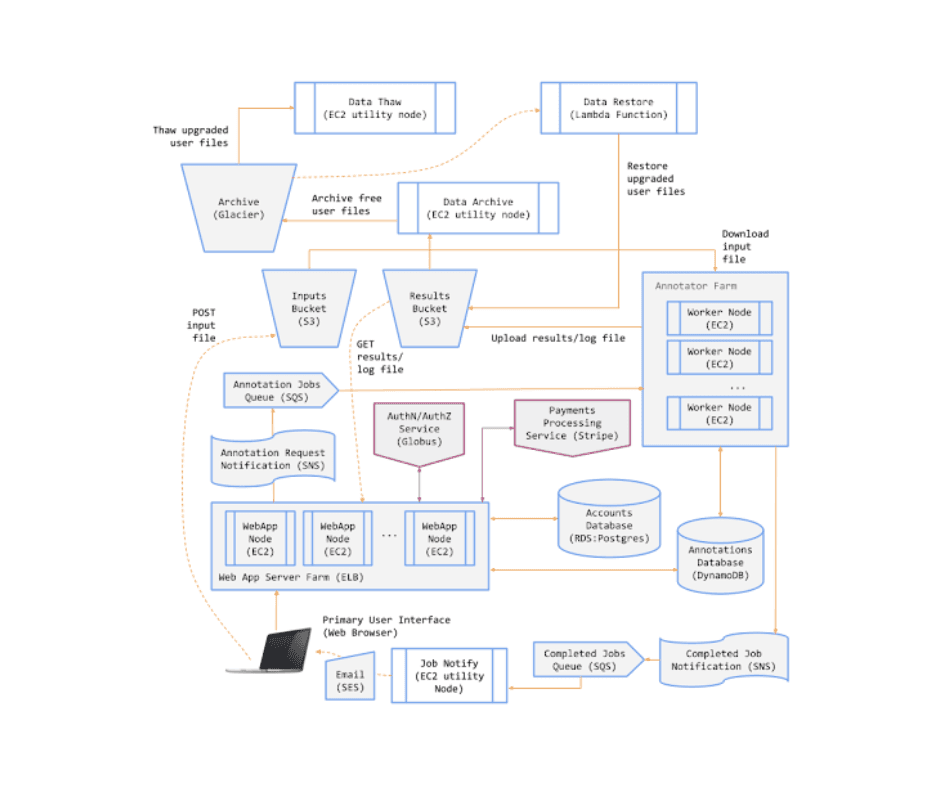
Components of the Genomics Analysis Service (GAS)
AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Stores input files, annotated (result) files, and job log files.
DynamoDB
Key-value store for persisting information on annotation jobs.
EC2 Utility Node
A low-cost, highly-durable object store used for archiving the data of free-tier users.
Relational Postgres Database
Stores user account information.
EC2 Instance Running AnnTools
Executes the AnnTools software for genomic annotation tasks.
Web Application
Provides an interface for users to interact with the GAS.
Message Queues and Notification Topics
Coordinates system activity and ensures efficient communication between components.
Technical highlight
Core Functionalities of GAS
User Authentication (via Globus Auth):
Users must log in to access the service.
Two user classes are supported: Free and Premium.
Free Users: Limited access to functionality.
Premium Users: Access to advanced features, such as larger file sizes and persistent storage of annotation result files.
Submit Annotation Jobs:
Free Users: Limited to jobs of a certain size.
Premium Users: Can submit jobs of any size.
If a Free user submits an oversized job, the system will:
Reject the job.
Prompt the user to upgrade to Premium.
Upgrade to Premium:
Users can upgrade from Free to Premium by providing payment details.
Payment Integration: Credit card payments are handled via Stripe.
Email Notifications for Completed Jobs:
Users receive an email when their annotation jobs are complete.
Email includes:
A link to view the log file.
A link to download the results file.
Job Browsing and Results Download:
Users can:
View a list of their jobs (both completed and running).
Access the log files of completed jobs.
Results are stored for later retrieval.
Data Access Restrictions for Free Users:
Free Users:
Can download results files for a limited time after job completion.
After the time limit, files are archived and only accessible upon upgrading to Premium.
Premium Users:
Always have full access to all their data for download.
Technical highlight
The Annotations Dashboard gives you a comprehensive overview of the different jobs and their statuses. The request ID can be clicked to view the details of the job.
Technical highlight
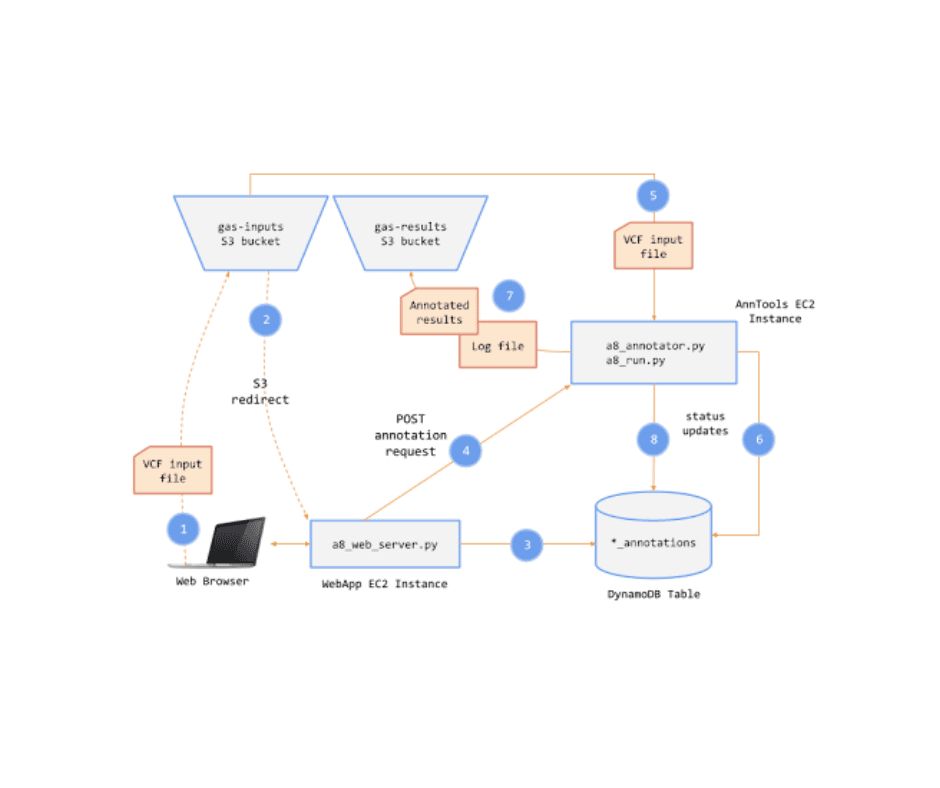
Automated Glacier File Thawing Architecture for Premium User Upgrades
When the details of a job are viewed, the results are available to the free tier users for only three minutes. I implemented an architecture that efficiently automates the thawing of genomic files stored in AWS Glacier when free-tier users upgrade to premium. The system leverages several AWS services, including SNS, SQS, Lambda, DynamoDB, and S3, ensuring reliable file retrieval and storage.
1. Premium User Upgrade Event
Trigger: When a user links their Stripe account to the Genomics Analysis Service (GAS) and upgrades to premium, an SNS topic
navyavedachala_a16_start_thawis triggered.Action: A message about the upgrade is published, initiating the thawing process.
2. Thaw Endpoint Subscription
Subscription: The /thaw API endpoint is subscribed to the SNS topic
navyavedachala_a16_start_thaw.Action: Upon receiving the upgrade notification, it begins processing the thaw request.
3. Polling from SQS Queue
Queue: An SQS queue
navyavedachala_a16_start_thawis subscribed to the SNS topic.Action: The queue polls for messages to ensure that every message is processed at least once, increasing reliability in case of downtime or errors.
4. Querying DynamoDB for Archived Files
Query: Within the /thaw endpoint, the DynamoDB table is queried for jobs that have an associated
results_file_archive_id.Optimization: The query avoids a full table scan, keeping costs minimal and efficiently retrieving relevant records.
5. File Information Extraction
Metadata Retrieval: The query extracts
s3_key_result_fileandjob_idfor the corresponding jobs.Purpose: This metadata is passed to the Glacier retrieval process for accurate file tracking and restoration.
6. Initiating Glacier Job
Action: For each archived file, a Glacier retrieval job is initiated using the
glacier_client.initiate_jobfunction.
7. Receiving Glacier Completion Notification
Completion SNS Topic: An SNS topic
navyavedachala_a16_complete_thawreceives messages from Glacier when a file retrieval is complete.SQS Queue Subscription: The SQS queue
navyavedachala_a16_complete_thawsubscribes to this topic and captures the completion messages.
8. Lambda Function for File Restoration
Trigger: The Lambda function
navyavedachala_a16_restoreis triggered by messages in the SQS queue.Action: It processes the completion notification and restores the file to S3.
9. Cleanup and Archive Deletion
Job Completion: Glacier provides a
glacier_job_idupon successful retrieval.Lambda Actions: The Lambda function saves the retrieved file to S3, deletes the archived file from Glacier, and removes the message from the SQS queue.
10. Frontend Integration
Status Reflection: The frontend displays the status of the file restoration to the user.
Takeaways